COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF Y495 & G496 MUTANTS
Y495: The mutations at Y495 site of 2019-nCoV-S1 could not directly interact with any amino acids on ACE2, because the sidechains oriented themselves to the opposite direction of binding interface. Therefore, most of the mutated systems except Y495E could not form interactions with ACE2 (Figure 7A). However, when the residue Y495 was mutated to E495, E495 formed one strong salt-bridge with distant K353, which would be analyzed in subsequent experiments (Figure 7B).
G496: The RMSD values for all mutant systems at position 496 on 2019-nCoV-S1 changed significantly, indicating that the structure of the surrounding area changed considerably. According to the structural analysis, G496 was enclosed by multiple amino acids Q498, N501, F497, N448, Y449, Y495, K353, and D38 (Figure 7C). However, mutations were likely to cause conformation changes of protein structures. Any mutation that might destroy the original structures will not be analyzed in this paper.
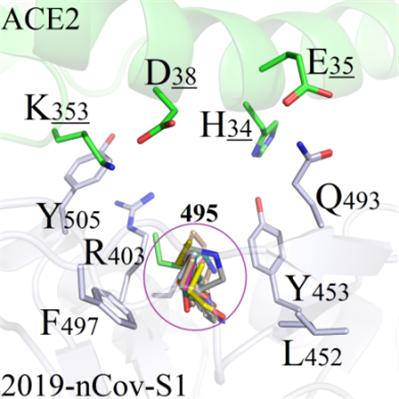 A(Y495)
A(Y495)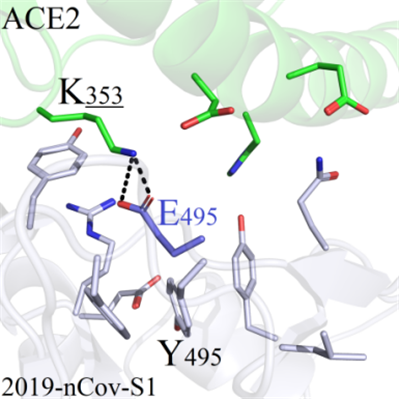 B(Y495)
B(Y495) C(G496)
C(G496)Figure 7. Binding modes comparison of regional structure near mutation site Y495.