COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF N487 MUTANTS
In this series, amino acid N487 in wild complex formed internal hydrogen bonds with neighboring Y83 and Q24 (Figure 4A), thus Y83 and Q24 were selected as reference for comparison analysis of the structure stability:
(a) Hydrophobic amino acids CGPAVI and LMFYW could not compensate for the polar environment of Q24 in terms of physical and chemical properties, and the RMSD values changed greatly (Figure 4B).
(b) Relatively tiny structural changes were observed in N487S/T/Q mutants. Altough residues S487, Q487 and T487 could form hydrogen bonds with Q24, but both of them could not form hydrogen bonds with Y83, nor could they form the hydrophobic interactions with F486, which resulted in weakened binding affinities in these mutants (Figure 4C).
Here, no suitable mutant systems were selected for subsequent analysis.
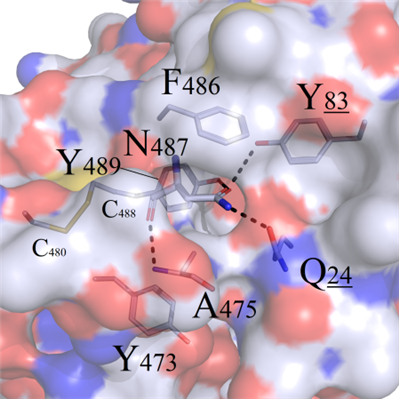 A
A B
B C
CFigure 4. Comparison analysis between wild-type and N487 mutated complexes. (A) Surface map of hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties around the F487 site (white: hydrophobic); (B) Selected residues: positive R486, negative E486 and uncharged polar Q486, compared with F486; (C) Hydrophobic short sidechain residues M486 and I486, compared with F486; (D) Hydrophobic long sidechain residues W486 and Y486, compared with F486.