COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF G446 MUTANTS
As shown in Figure 1, the mutation site G446 was located in the peripheral region of the 2019-nCoV-S1/ACE2 binding interface, thus tiny conformation differences were observed for all complexes. Among 19 mutant systems, the RMSD values of amino acids within 5Å from the mutation site were less than 0.216. Only 3 systems (G446F, G446Q and G446R) presenting little difference compared with the wild-type protein were selected for detailed analysis: For mutant G446F, the sidechain on residue F446 formed hydrophobic interactions with surrounding residues including V445 (Figure 1A). One new hydrogen bond was formed between K444 and N446 in mutant system G446Q (Figure 1B). However, both the conformation presented slight perturbations as the binding patterns between 2019-nCoV-s1 and ACE2 was not affected. Regional structure was disturbed after mutation, as the mutated amino acid R446 formed a new type of hydrogen bond with Q42, which was stronger than that of the wild-type weak hydrogen bond interaction between G446 and Q42 (Figure 1C).
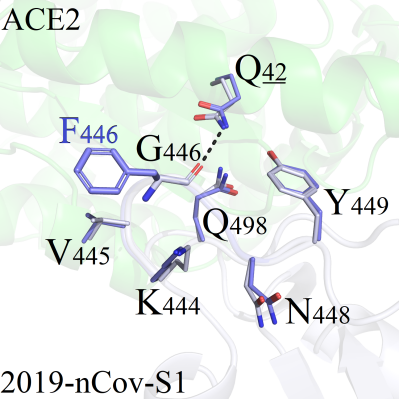 A(G446F)
A(G446F)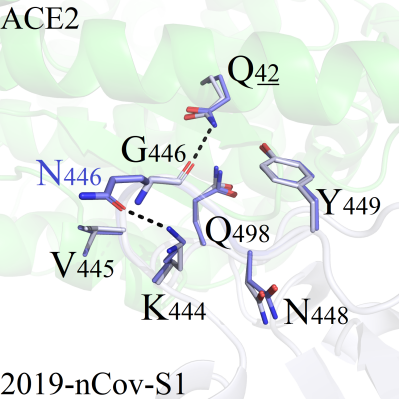 B (G446Q)
B (G446Q) C (G446R)
C (G446R)Figure 1. Binding patterns comparison of G446 series mutant systems. 2019-nCoV-S1: white, sticks; A CE2 protein: green, sticks, underlined. The Q42 amino acid was located on the ACE2 protein, and other residues were located on the 2019-nCoV-S1 protein.