| • DyNetViewer | |
|---|---|
|
| • CytoNCA | |
|---|---|
|
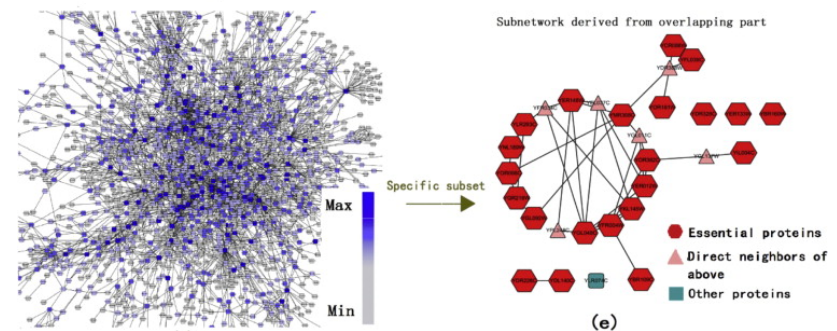
CytoNCA supports eight different centrality measures and each can be applied to both weighted and unweighted biological networks.It allows users to upload biological information of both nodes and edges in the network, to integrate biological data with
topological data to detect specific nodes.
[Link]
[Paper]
|
| • Cytocluster | |
|---|---|
|
| • ClusterViz | |
|---|---|
|
| • CytoCtrlAnalyser | |
|---|---|
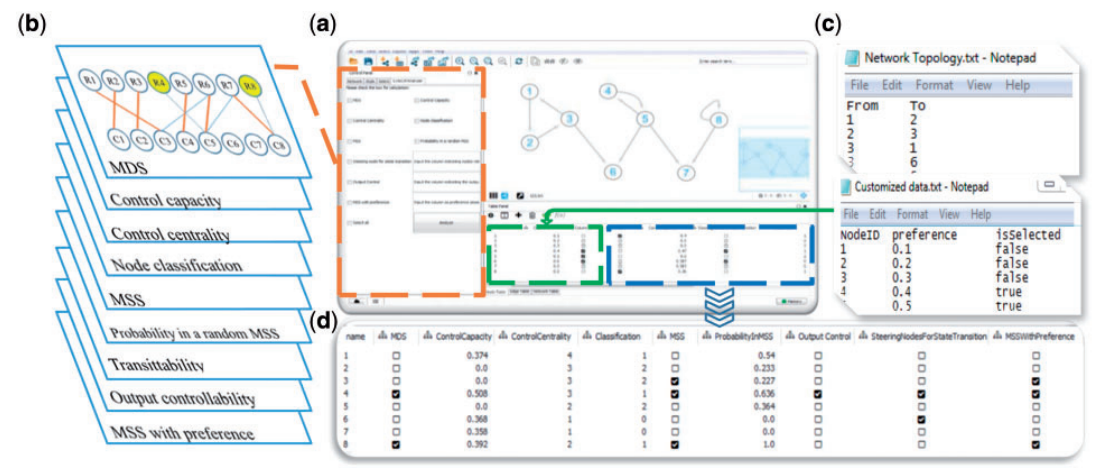
|
| • HC-PIN | |
|---|---|
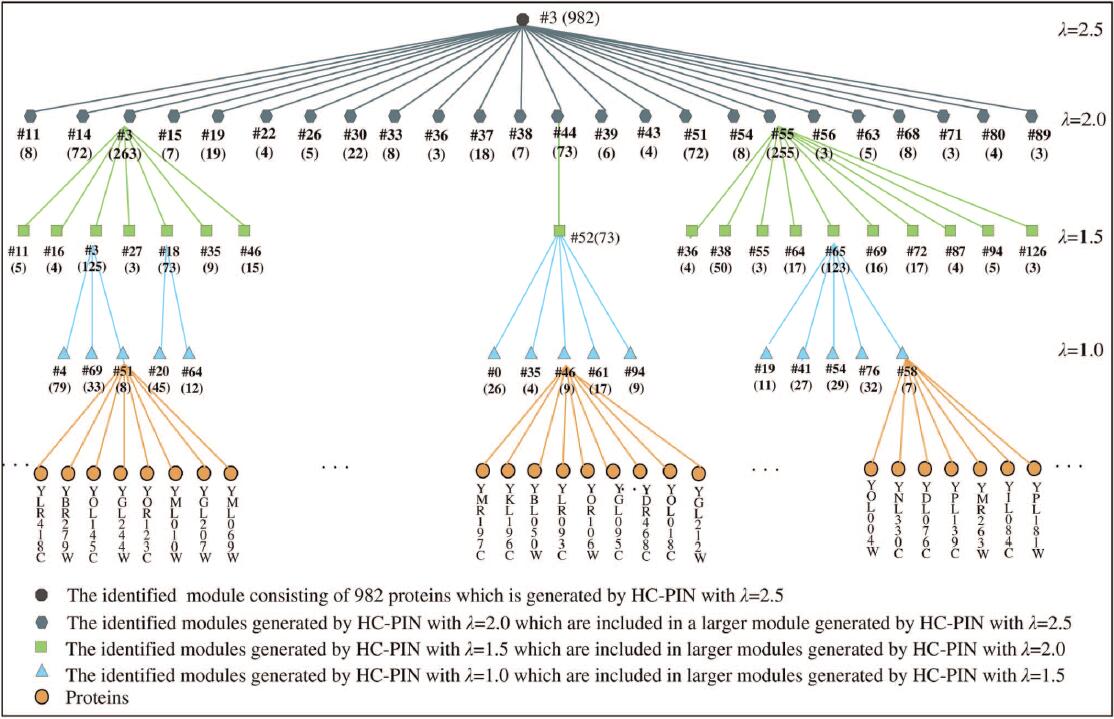
|
| • DFM-CIN | |
|---|---|
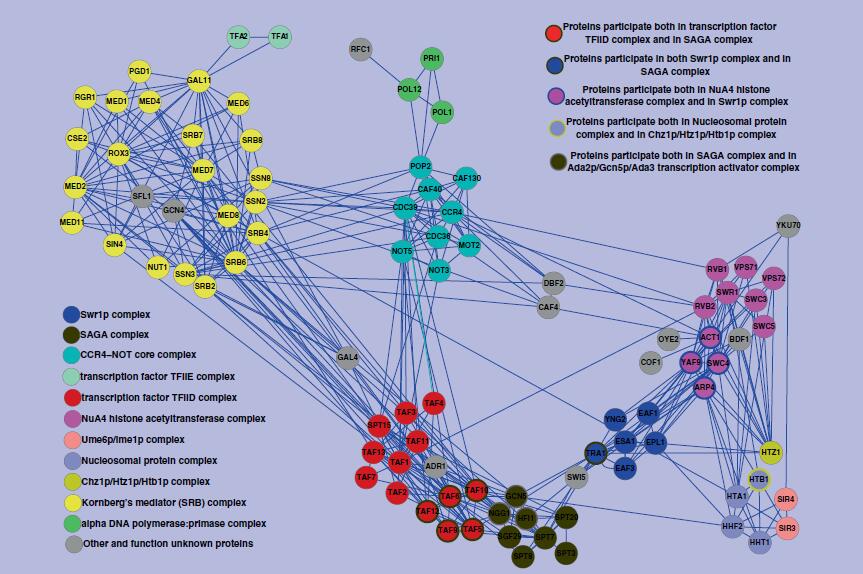
|
DFM-CIN is a new framework to distinguish between protein complexes and functional modules by integrating gene expression data into protein-protein interaction (PPI) data. A series of time-sequenced subnetworks (TSNs) is constructed according to the time
that the interactions were activated.
[Link]
[Paper]
|
| • IPCA |
|---|
| • LoopPredictor | |
|---|---|
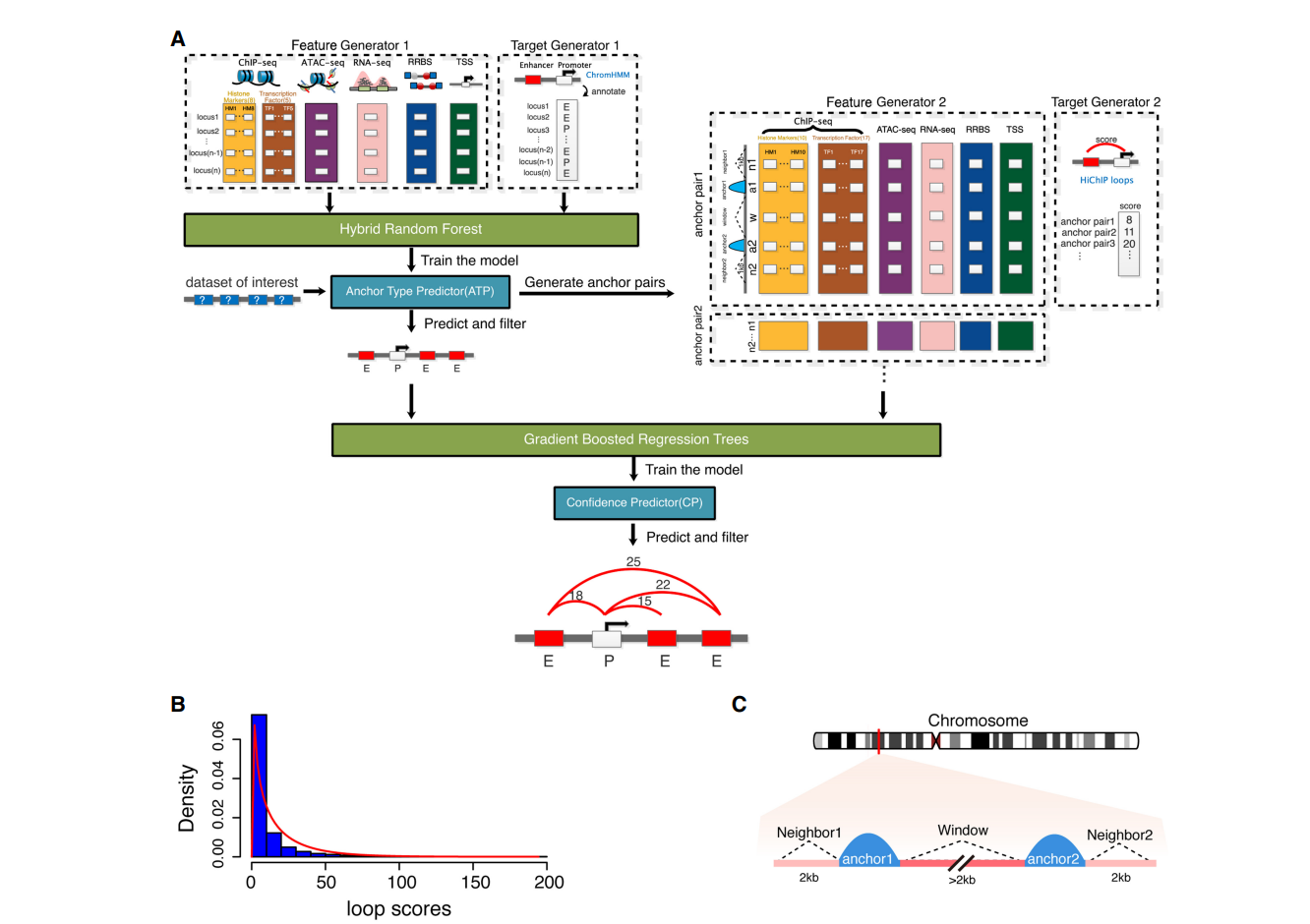
|
| • NID | |
|---|---|
|
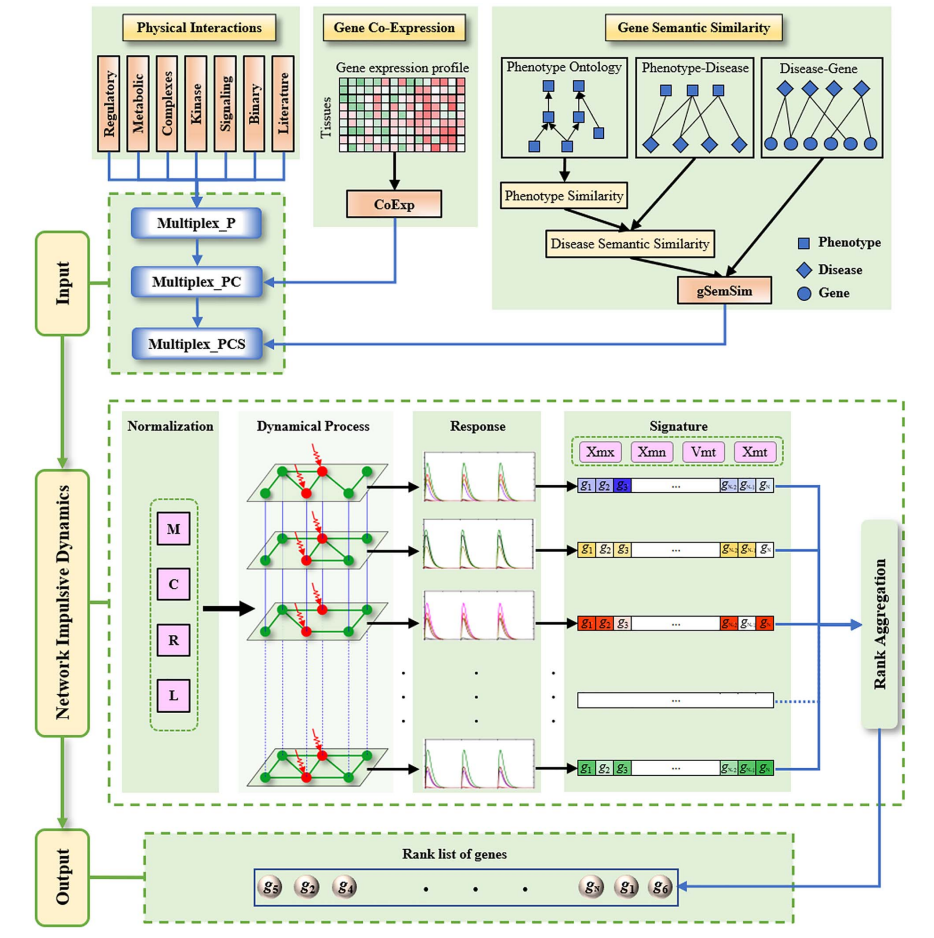
NID is a comprehensive user-friendly web server for the prioritization and analysis of disease-related (candidate) genes, by which the users can easily get the results of disease-related genes by three search patterns (genomic location, cytogenetic location
and whole network genome), subnetwork visualization, enrichment analysis and external links of the genes.
[Link]
[Paper]
|
| • NIDM |
|---|
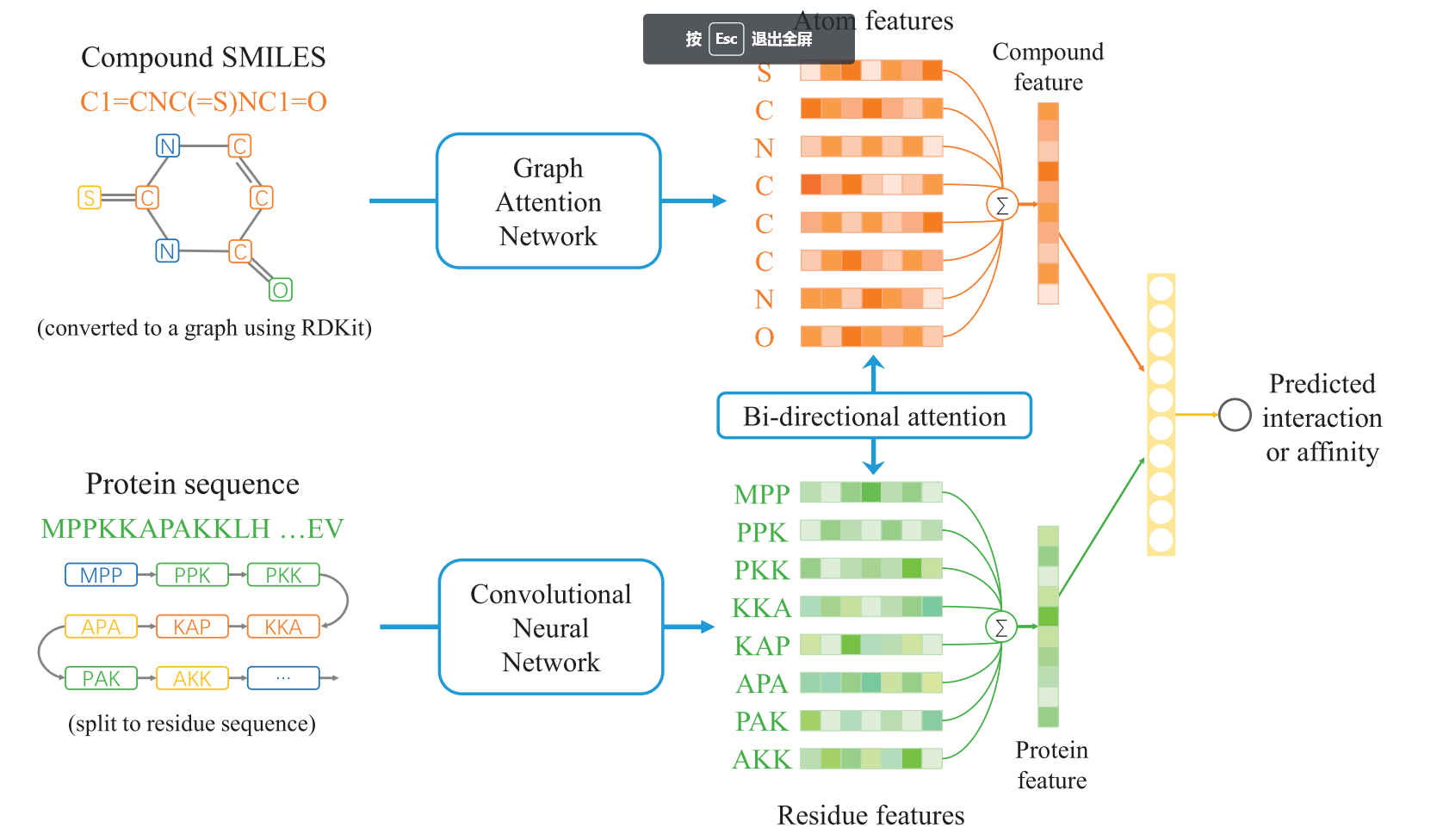
| • BACPI | |
|---|---|
|
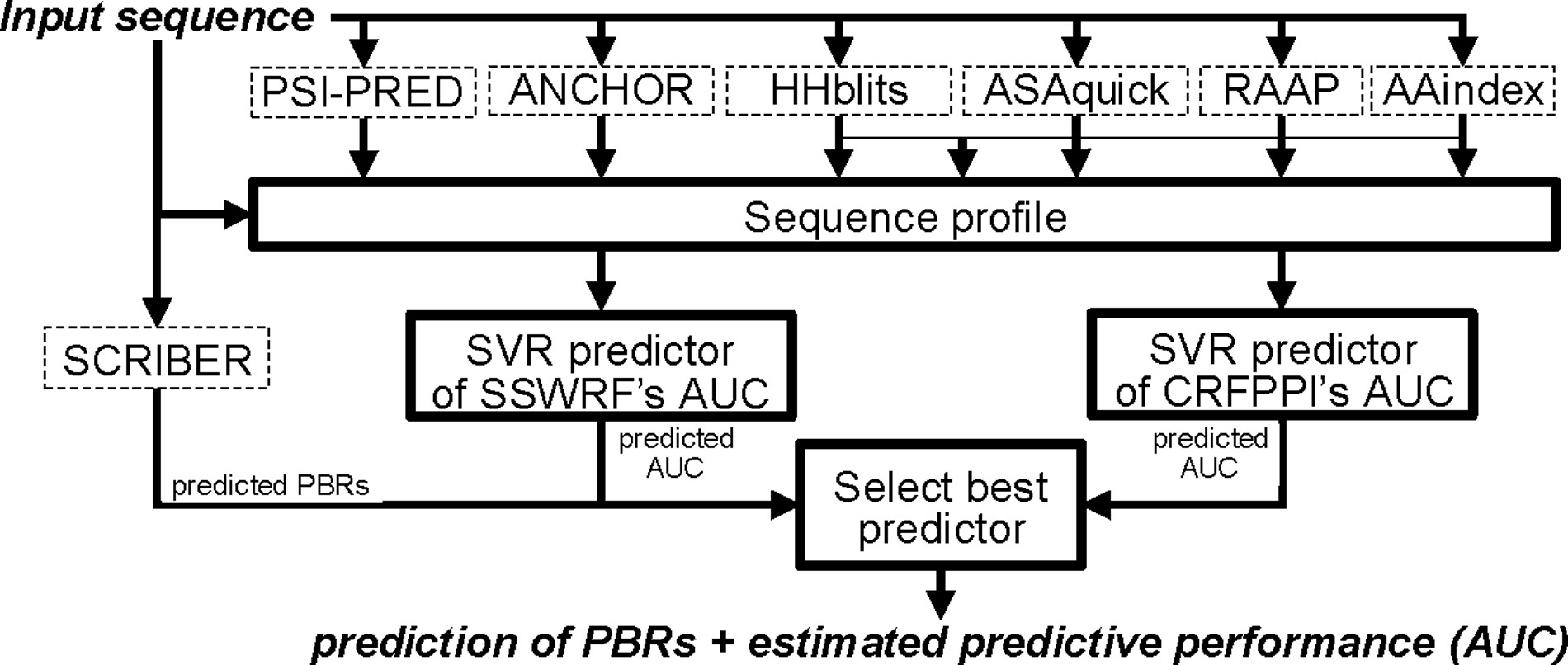
| • PROBselect | |
|---|---|
|
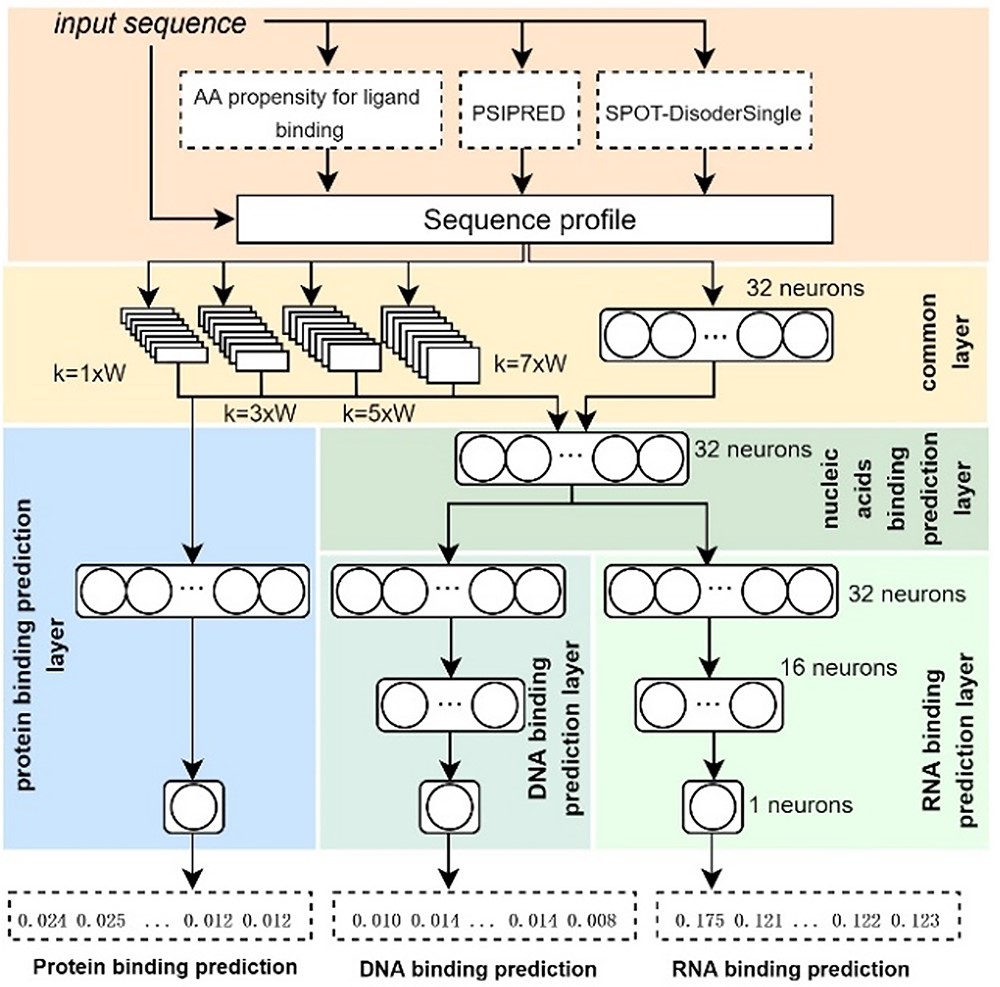
| • DeepDISOBind | |
|---|---|
|
| • DeepDTAF |
|---|
| • DeepPFP-CO |
|---|
|
DeepPFP-CO uses Graph Convolutional Network to explore and capture the co-occurrence of GO terms to improve the prediction of protein function.
[Link]
|
| • SSRE | |
|---|---|
|
| • NIMCE | |
|---|---|
|
| • SinNLRR | |
|---|---|
|
| • BiXGBoost | |
|---|---|
|
| • DeepLncLoc | |
|---|---|
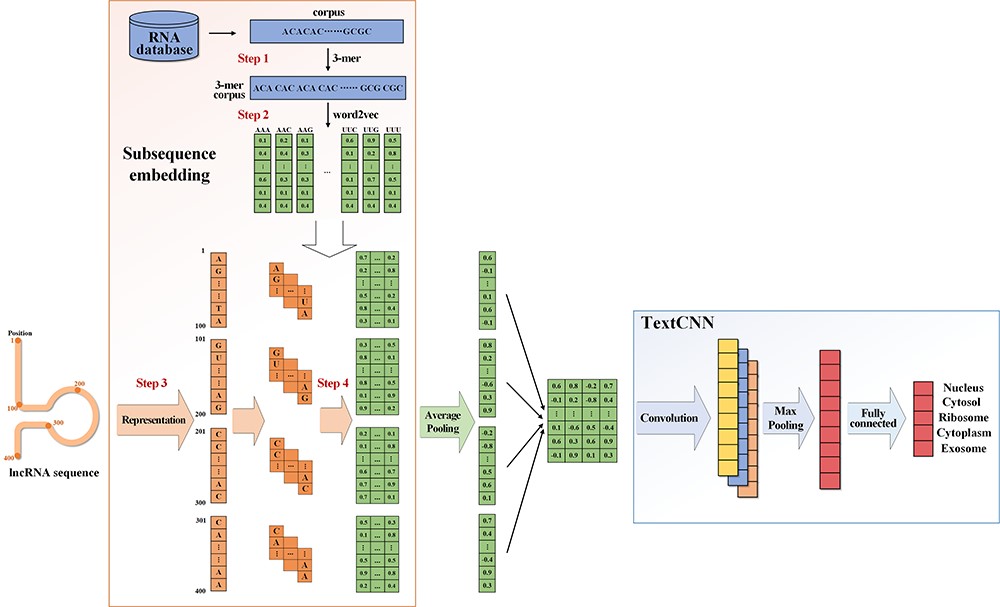
|
| • EP-GBDT | |
|---|---|
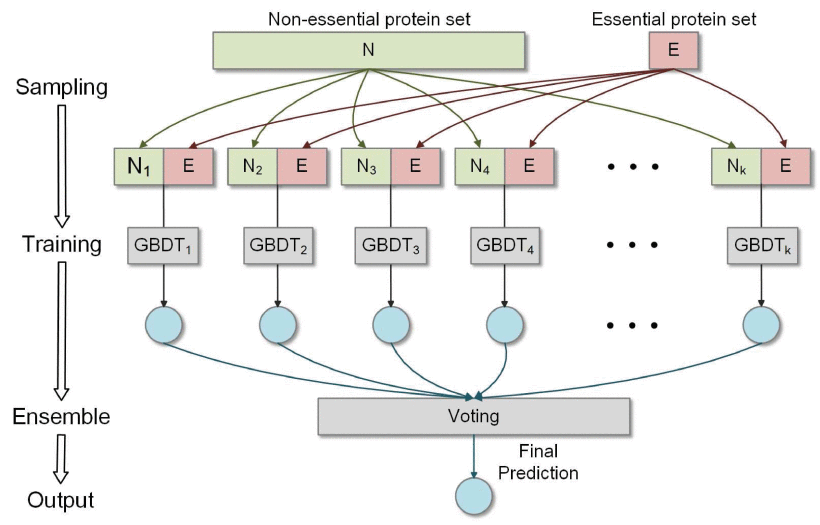
|
| • SCOP |
|---|
| • MAC |
|---|
| • iLSLS |
|---|
| • HyMM |
|---|
| • PrGeFNE |
|---|
| • DPCMNE |
|---|
| • TemporalspatialHub |
|---|
|
Temporal-spatial analysis of the essentiality of hub proteins in protein-protein interaction networks.
[Link]
|
| • NetEPD |
|---|
| • CPPK&CEPPK | |
|---|---|
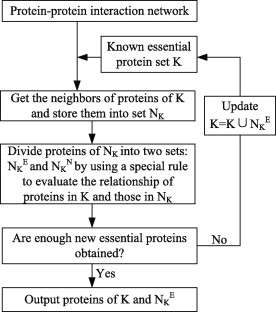
|
| • PeC |
|---|
| • LAC |
|---|
| • MBiRW | |
|---|---|
|
MBiRW is a novel computational method named to utilizes some comprehensive similarity measures and Bi-Random walk (BiRW) algorithm to identify potential novel indications for a given drug. By integrating drug or disease features information with known
drug-disease associations, the comprehensive similarity measures are firstly developed to calculate similarity for drugs and diseases.
[Link]
[Paper]
|
| • DRRS | |
|---|---|
|
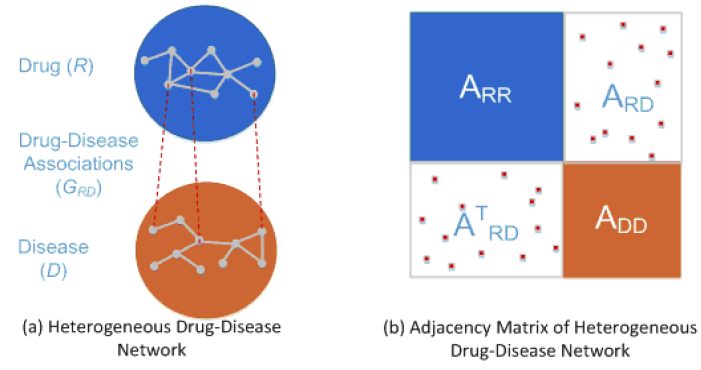
DRRS is a drug repositioning recommendation system, which can complete the association matrix of drug-disease heterogeneous network based on the Singular Value Thresholding (SVT) algorithm. A recycling rank revealing randomized singular value decomposition
algorithm (R4SVD) is employed to fast and adaptively approximate the dominant singular values and their associated singular vectors so that the recommendation system is scalable to handle large adjacency matrices generated
from large-scale drug-disease networks.
[Link]
[Paper]
|
| • RWHNDR | |
|---|---|
|
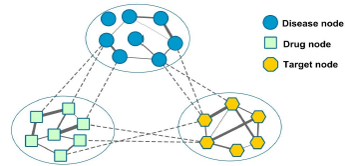
RWHNDR is a novel drug repositioning method by implementing random walk on the drug-target-disease network. By integrating multi-source data and exploiting global heterogeneous network information, it can predict and prioritize potential drugs for diseases
effectively.
[Paper]
|
| • PUDT |
|---|
| • SIMCLDA | |
|---|---|
|
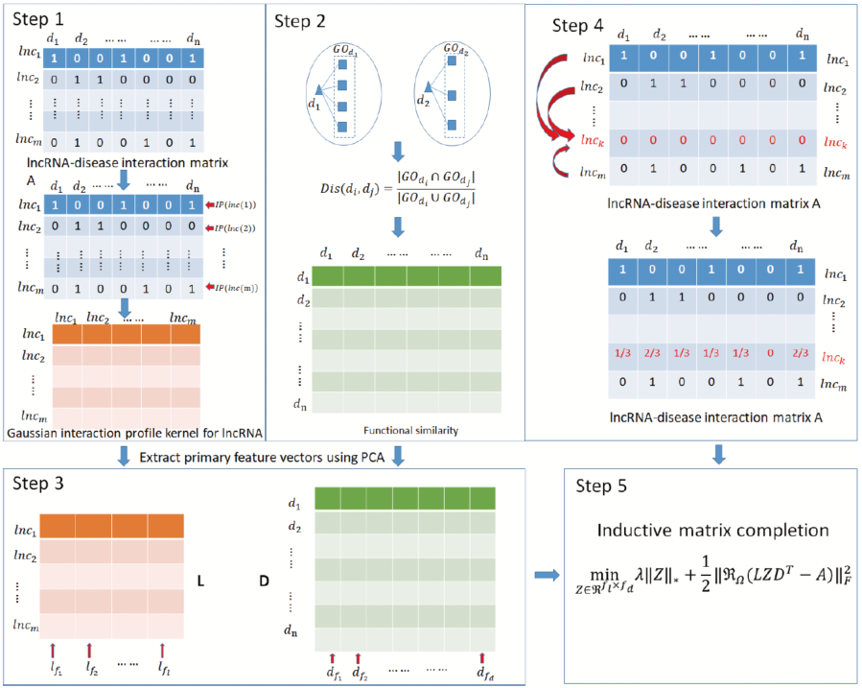
SIMCLDA is a method to predicte potential lncRNA-disease associations based on inductive matrix completion. We compute Gaussian interaction profile kernel of lncRNAs from known lncRNA-disease interactions and functional similarity of diseases based on
disease-gene and gene-gene onotology associations. Then, we extract primary feature vectors from Gaussian interaction profile kernel of lncRNAs and functional similarity of diseases by principal component analysis, respectively.
[Link]
[Paper]
|
| • ISEA | |
|---|---|
|
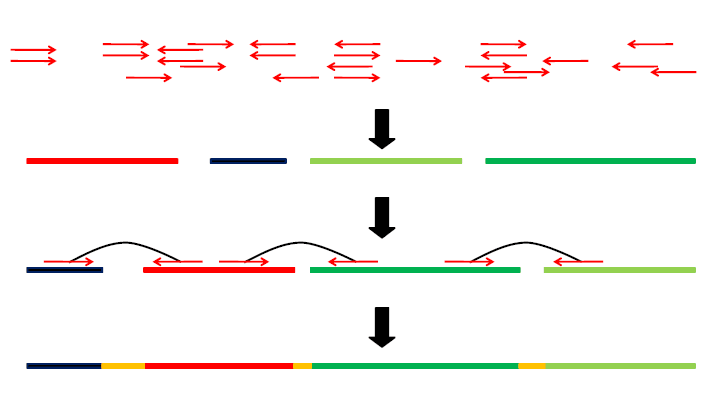
ISEA is an iterative seed-extension algorithm for de novo assembly, ISEA utilizes reads overlap and paired-end information to correct error reads before assemblying, and uses an elaborately designed score function based on paired-end information and the
distribution of insert size to solve the repeat region problem.
[Link]
[Paper]
|
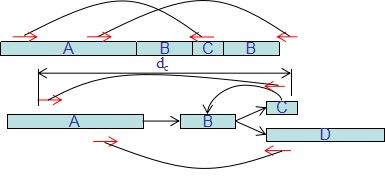
| • EPGA | |
|---|---|
|
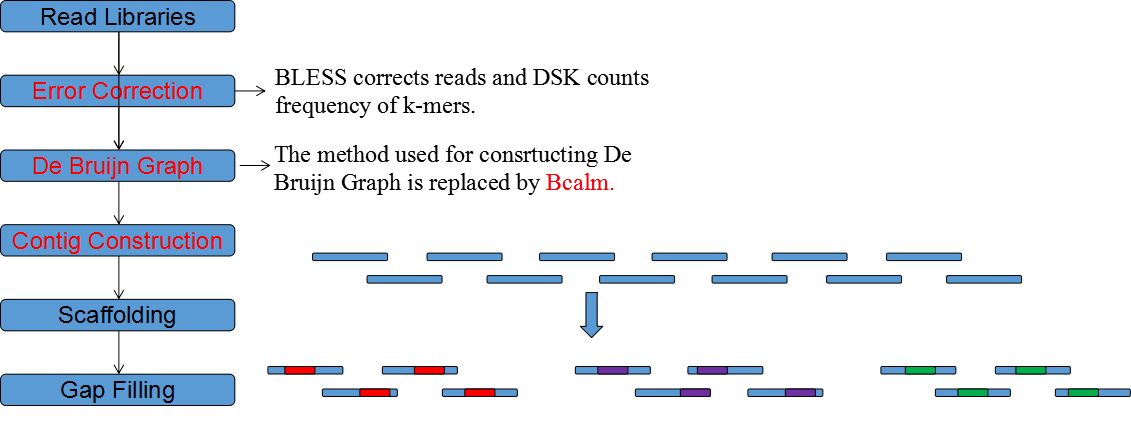
| • EPGA2 | |
|---|---|
|
EPGA2 is an updated version of EPGA, which applies some new modules and can bring about improved assembly results in small memory. EPGA2 adopts memory-efficient DSK to count K-mers and revised BCALM to construct De Bruijn Graph. Moreover, EPGA2 parallels
the step of Contigs Merging and adds Errors Correction in its pipeline.
[Link]
[Paper]
|
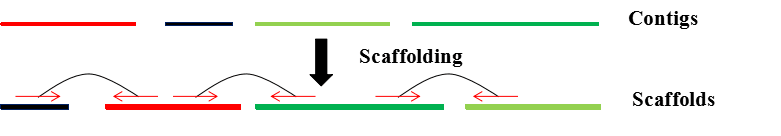
| • BOSS | |
|---|---|
|
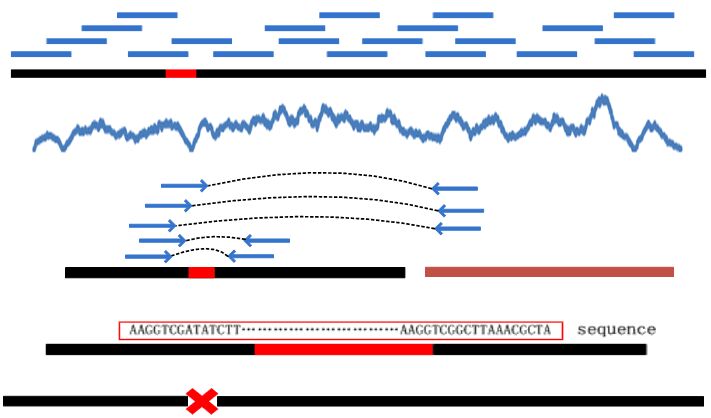
| • MEC | |
|---|---|
|
| • PECC | |
|---|---|
|
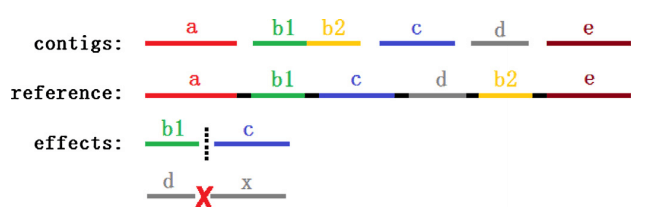
PECC identifies and corrects misassembly errors in contigs based on the paired-end read distribution. PECC extracts sequence regions with lower paired-end reads supports and verifies them based on the distribution of paired-end supports.
[Paper]
|
| • GapReduce | |
|---|---|
|
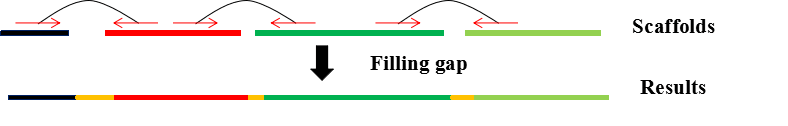
GapReduce is a gap filling method, which can fill the gaps using the paired reads, and GapReduce designs a novel approach that simultaneously considers k-mer frequency and distribution of paired reads based on the partitioned read sets.
[Link]
|
| • LDAP | |
|---|---|
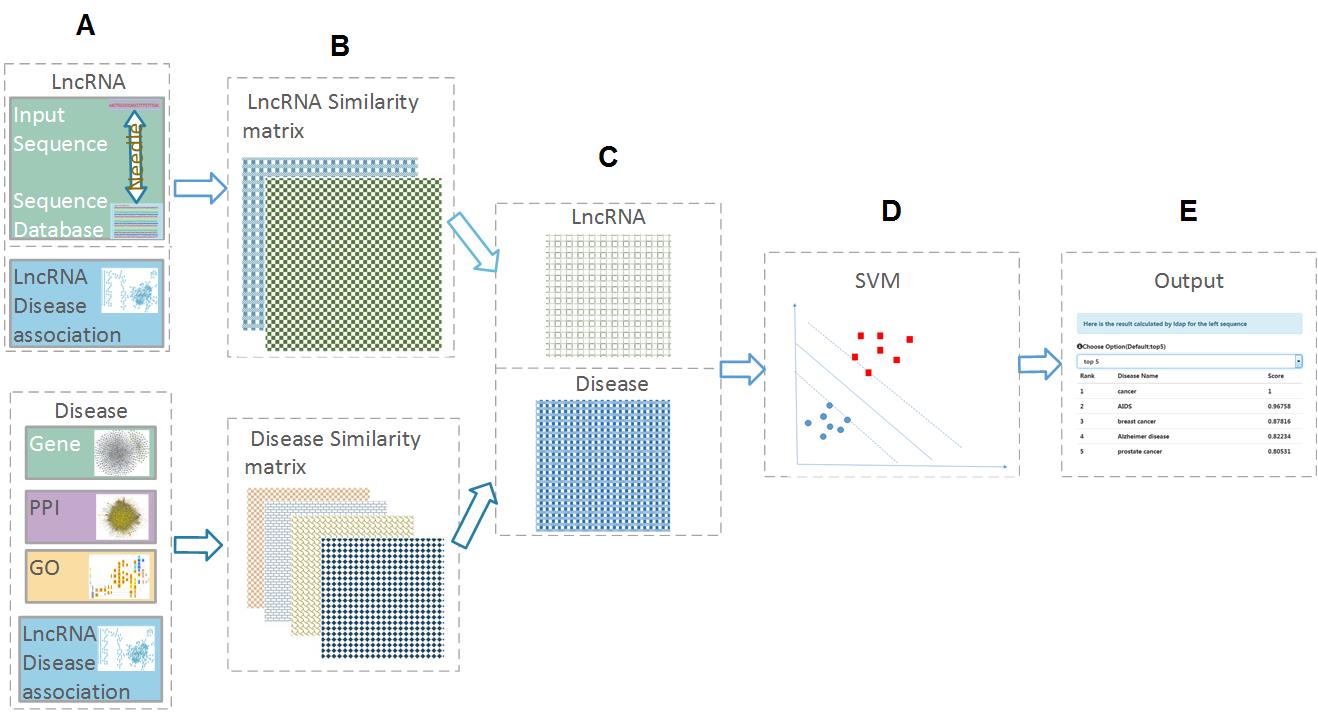
|
| • CSA | |
|---|---|

|
CSA is developed for the whole process of ChIP-Seq analysis, which covers mapping,quality control,peak calling and downstream analysis.In addition,CSA provides a customization function for users to define their own workflow.Moreover,the visualization
of mapping,peak calling, motif finding,and pathway analysis results is also supplied in CSA.
[Link]
|